<img class="aligncenter" src="https://scx1.b-cdn.net/csz/news/800a/2023/precarious-employment.jpg"
alt="Precarious employment conditions can increase risk of early death"
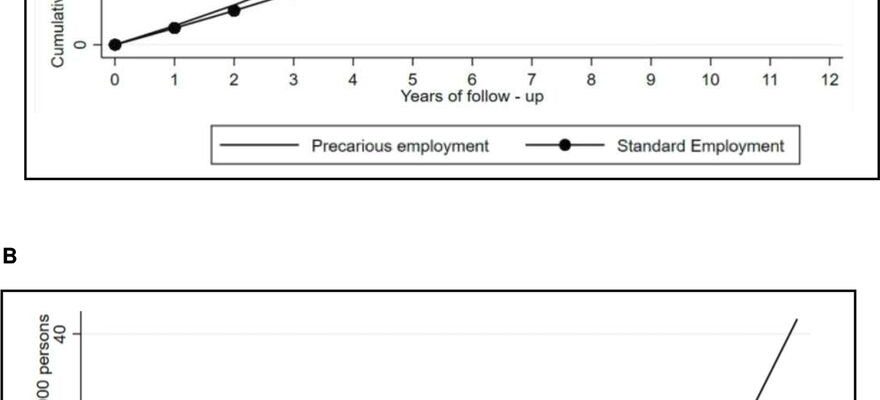
title="Standardized risk curves comparing shifting to standard employment versus remaining in precarious employment, 2005–2017. (A) Observational analog to an intention-to-treat analysis. Risk curves standardized for baseline covariate distribution. Note: risk curve standardized for baseline covariate distribution (age, level of education, sex, health diagnoses, family composition, unemployment spells). (B) Observational analog to per-protocol analysis. Risk curves standardized for baseline covariate distribution and weighted for time-varying confounders. Note: risk curve standardized for baseline covariate distribution (age, lexapro zoloft weight gain level of education, sex, health diagnoses, family composition, unemployment spells) and weighted for time-varying confounding. Credit: Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health (2023). DOI: 10.1136/jech-2023-220734″ width=”800″ height=”528″>
People without a secure job contract can reduce their risk of premature death by 20 percent if they gain permanent employment, a study from Karolinska Institutet published in the Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health reports. According to the researchers, the results indicate that job security on the Swedish labor market needs to improve.
Precarious employment is a term that is used to describe jobs with short contracts (e.g. temping), low wages and a lack of influence and rights, all of which lead to a working life without predictability and security.
In the present study, the researchers have examined how this affects the risk of death.
“This is the first study to show that changing from precarious employment to secure employment can reduce the risk of death,” says the paper’s last author Theo Bodin, assistant professor at the Institute of Environmental Medicine, Karolinska Institutet. “It’s the same as saying that the risk of early death is higher if one keeps working in jobs without a secure employment contract.”
The researchers used registry data from over 250,000 workers in Sweden between the ages of 20 and 55 gathered over a period from 2005 to 2017. The study included people who worked under insecure working conditions and who then shifted to secure working conditions.
Those who switched from precarious to secure employment had a 20 percent lower risk of death, regardless of what happened afterward, compared to those who remained in precarious employment. If they remained in secure employment for 12 years, the risk of death decreased by 30 percent.
“Using this large population database allowed us to take account of many factors that could influence mortality, such as age, other diseases that workers can suffer from or life changes like divorce,” explains Nuria Matilla-Santander, assistant professor at the same institute and the study’s first author. “Because of the methods we used, we can be relatively certain that the difference in mortality is due to the precariousness of employment rather than individual factors.”
“The results are important since they show that the elevated mortality rate observed in workers can be avoided. If we reduce precariousness in the labor market, we can avoid premature deaths in Sweden.”
Dr. Matilla-Santander says that the next stage of the research is to examine the specific causes of mortality in this regard.
More information:
Nuria Matilla-Santander et al, Causal effect of shifting from precarious to standard employment on all-cause mortality in Sweden: an emulation of a target trial, Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health (2023). DOI: 10.1136/jech-2023-220734
Journal information:
Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health
Source: Read Full Article