A recently published set of treatment flow diagrams uses simplified diagnosis and management pathways to help primary care providers (PCPs) in Europe, the United States, and elsewhere treat patients with allergies.
Most patients with allergy problems first see PCPs, not allergists, the authors write in Allergy. The new flow diagrams help PCPs treat anaphylaxis, asthma, drug allergy, food allergy, and urticaria.

Dr Dermot Ryan
“The European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology (EAACI) established the Logogram Task Force to create a set of simple flow diagrams to assist allergy nonspecialist, generalist, and primary care teams in the diagnosis of five common allergic diseases encountered in primary care,” lead author Dermot Ryan, MB BCh, BAO, FRGCP, of the University of Edinburgh, United Kingdom, told Medscape Medical News.
“The source documents were mainstream guidelines coupled with ancillary literature,” he added in an email. “A multi-disciplinary taskforce…distilled these guidelines into accessible, comprehensible, usable, and context-specific flow diagrams.”
The Flow Diagrams Developed in Europe Can Be Used by Providers in the US and Elsewhere
“These diagrams are consistent with practices in the US,” Christina E. Ciaccio, MD, an associate professor of pediatrics and the section chief of pediatric allergy and immunology at the University of Chicago Medicine, said in an email. “They will prove helpful to PCPs in the US and elsewhere, particularly to young physicians new to practice.

Dr Christina Ciaccio
“Treating allergies is part of the ‘bread-and-butter’ practice of primary care physicians in the US,” Ciaccio, who was not involved in developing the flow diagrams, explained. “Up to 30% of Americans are atopic, and the vast majority seek treatment advice from their PCP first.”
The flow diagrams can help providers in developing countries, where allergic diseases are common, provide the best patient care possible, she said.
At Some Point, a PCP May Need to Think Beyond Flow Diagrams and Refer the Patient to an Allergist
“If the treatment plan for a patient falls outside first- or second-line medications, or if a diagnosis is unclear with preliminary testing, a PCP may reach out to an allergy/immunology specialist to assist in providing care,” Ciaccio advised. “Allergists may provide treatment options, such as immunotherapy, that the PCP does not offer. PCPs also often reach out to allergy team members for help with patients whose allergies are not ‘run-of-the-mill.’
“The flow diagrams are complex and may not be practical in the middle of a busy clinic,” she cautioned. “However, when a patient comes into a primary care clinic with an atypical presentation of an allergic disease, the diagrams are likely to help a physician feel confident that an allergist is the right physician for consultation.”

Dr Patricia Lynne Lugar
Patricia Lynne Lugar, MD, an associate professor of medicine in pulmonary, allergy, and critical care medicine at Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina, noted that providers in the US can use the flow diagrams because the definitions, differential diagnosis, and treatments for the conditions they cover are similar.
“The flow diagrams are comprehensive, and they attempt to condense a great deal of information into summary points. They are very useful in the US, and not just for generalists,” Lugar, who also was not involved in the project, said. “Even emergency rooms would benefit from these flow diagrams, especially regarding the recognition of symptoms and differential diagnosis.”
Asthma and seasonal and environmental allergies are often managed by PCPs, and the flow diagrams would help them decide when to refer their patients to an allergist, she added in an email.
Lugar advises PCPs to “recognize the symptoms of an allergic condition, offer treatment based on confidence the diagnosis is correct, and offer a referral for testing to confirm the allergy.
“Because 50% or more of asthmatics are allergic, all asthmatics should be offered an allergy evaluation to determine their allergies and avoid exacerbating the asthma,” she added. “I do not see the flow diagrams as comprehensive enough to manage chronic urticaria, asthma, venom allergy, and drug allergy.”
With food allergy, environmental allergy, venom allergy, or anaphylaxis, “allergists are experts at considering the differential diagnosis and providing the next steps in the diagnostic workup,” Lugar said. “Allergists can also provide special treatments, such as allergen-specific immunotherapy or desensitization.”
The flow diagrams guide nonspecialists in diagnosis and treatment of their patients with allergy, with supplementary information as needed. The diagrams recommend referral to a specialist when appropriate, as in cases of anaphylaxis, or chronic urticaria.
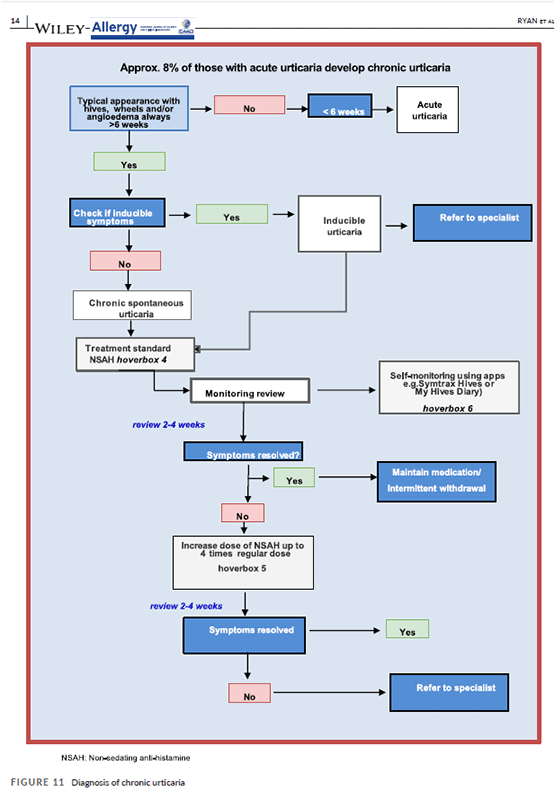
Providers searching for the most detailed guidance in the flow diagrams need to read information provided in five separate supplements. The development team plans to enable readers to access that information electronically by hovering over specific “hover boxes” in the charts. The flow diagrams need to be validated in clinical settings.
The task force was funded by EAACI. Ryan and several other authors report financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies. Ciaccio and Lugar report no such relationships.
Allergy. Published online March 10, 2022. Full text
For more news, follow Medscape on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and YouTube.
Source: Read Full Article
