A screening tool developed at the University of Strathclyde, U.K., could increase the number of tests on a solid tumor sample by up to 50 times.
The tool facilitates large scale testing of the latest immunotherapies, such as Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, which is effective against many hematological cancers but presents challenges when used to treat solid tumors.
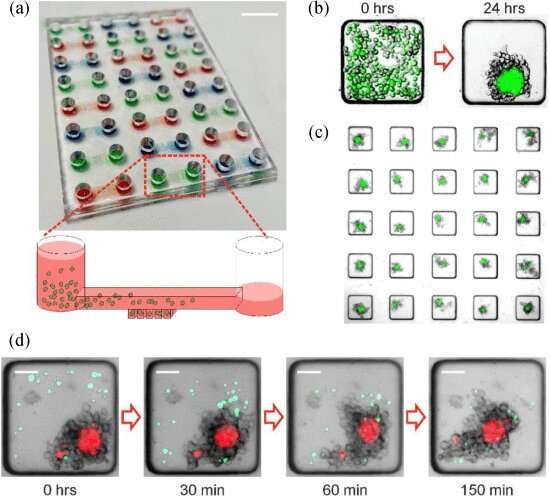
Currently used, traditional 2D models fail to reproduce the complexity of the tumor’s microenvironment, while models based on patients’ tumors are costly and labor-intensive; 3D models reproduce significantly better what happens in the body.
The Strathclyde-led study has developed a miniaturized platform for screening 3D tumor models to evaluate the toxicity of CAR-T therapy towards cells. The platform enabled visualization and quantification of how CAR-T cells rapidly targeted, broke up and killed cancer cells without causing significant harm to other cells.
In addition, the research found that, while chemotherapy treatment did not act specifically on cancer cells when used alone, treatment efficacy was enhanced when combined with CAR-T cell treatment.
Combination therapies represent a huge opportunity for cancer medicine and this technology will aid pharma companies’ efforts to look for new treatments.
The study also involved researchers at the University of Glasgow and the Cancer Research UK Beatson Institute in Glasgow, led by Dr. Seth Coffelt. The work has been published in the IEEE Open Journal of Engineering in Medicine and Biology.
The research was led by Dr. Michele Zagnoni, a Reader in Strathclyde’s Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, and recently graduated Ph.D. student Karla Paterson.
Dr. Zagnoni said: “There are particular challenges with evaluating solid tumors, not just cancerous cells but those surrounding them.
“We are developing a technology platform which could accelerate the development of therapies and provide models which are much more representative of what happens in the body than what is currently available.
“We are providing a platform for labs to conduct tests before proceeding to clinical trials, that uses fewer resources and can scale up cost effectively.
Source: Read Full Article
