Heartburn is a symptom rather than a disease. It is a symptom of Gastro-esophageal reflux disease or “acid reflux”. This is a common condition when the acid produced in the stomach leaks out and seeps back into the esophagus or food pipe.
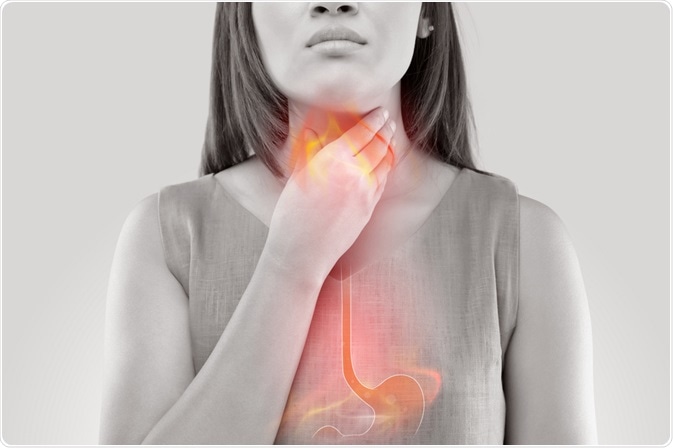 Image Credit: Emily frost / Shutterstock.com
Image Credit: Emily frost / Shutterstock.com
The esophagus is a tube made up of muscles and lined with a sensitive mucosal layer that runs from the mouth to the stomach. As the stomach’s acid leaks into the esophagus, it leads to heartburn or burning chest pain and discomfort. Despite the fact that the pain has nothing to do with the heart, its location is the reason for the nomenclature.
The leakage of the acid into the esophagus also leads to a sour or bitter taste in the back of the mouth and in severe cases pain and difficulty swallowing. Most people have stomach acid reflux at some point in their lives, either as heartburn or acid regurgitation.
Causes of heartburn
Acid reflux or heartburn may be caused due to multiple factors. Normally the esophagus is guarded at its lower end by a valve-like gate called the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). The LES acts like a valve, opening to allow food to be pushed into the stomach. It closes to prevent acid leaking out of the stomach and into the esophagus. In persons with acid reflux, the muscle of this sphincter may not be working properly.
In addition, those who are smokers, alcoholics, take pain relievers like Ibuprofen, consume a spicy or high-fat diet, or are obese, overweight or pregnant, are at a greater risk of getting acid reflux and heartburn.
Caffeine-containing foods like chocolates, coffee and peppermint also weaken the LES. Some people get heartburn when they bend over or lie down.
The frequency of stomach acid reflux varies from one person to another. The risk rises with age and may significantly decrease quality of life and overall well-being.
Risks associated with heartburn or acid reflux
If left untreated, the stomach acid can irritate the inner lining of the esophagus. This may lead to esophagitis. In more severe cases this may lead to open sores or ulcers within the esophagus. This is called erosive esophagitis. Over time, in rare cases, this may turn into cancers (esophageal cancer).
Treatment of heartburn
Treatment of acid reflux needs to include a major component of lifestyle change. Once this fails, therapy is stepped up to include antacids that help to neutralize the effects of stomach acid. Lifestyle changes include:
- quitting smoking
- reducing alcohol intake
- losing weight
- exercising regularly
- avoiding fatty and spicy foods etc.
Medications that reduce the secretion of the stomach acid called Proton Pump Inhibitors are one of the mainstays of therapy in acid reflux. Treatment of acid reflux is usually successful but relapses are common. Nearly half of the treated individuals experience a return of symptoms after a year.
Sources
- www.nhs.uk/…/Introduction.aspx
- http://digestive.niddk.nih.gov/ddiseases/pubs/gerd/gerd_508.pdf
- http://s3.gi.org/physicians/guidelines/GERDTreatment.pdf
- gastro.ucsd.edu/…/AGA%20guidelines%20on%20management[1].pdf
Further Reading
- All Heartburn Content
- Heartburn (Acid Reflux) Diagnosis
- Heartburn (Acid Reflux) Prevention
- Heartburn (Acid Reflux) Treatments
- Causes of Heartburn (Acid Reflux)
Last Updated: Jan 14, 2021

Written by
Dr. Ananya Mandal
Dr. Ananya Mandal is a doctor by profession, lecturer by vocation and a medical writer by passion. She specialized in Clinical Pharmacology after her bachelor's (MBBS). For her, health communication is not just writing complicated reviews for professionals but making medical knowledge understandable and available to the general public as well.
Source: Read Full Article
