![Distinct face and object representations in singly trained CNNs while a dual-task CNN performs well. (A) Three networks with VGG16 architecture (left) were optimized, one on face identity categorization (Face CNN in red), one on object categorization (Object CNN in orange), and one on both tasks simultaneously (dual-task CNN in gray). (B) Decoding accuracy of held-out face identities and held-out object categories using activation patterns extracted from the penultimate layer [i.e., FC2 in (A)] of the Face CNN and the Object CNN. The Face CNN outperforms the Object CNN in face decoding and vice versa for object decoding. Thus, the representations optimized for each task do not naturally support the other. The dashed gray line indicates chance level (1%). Error bars indicate SEM across classification folds. (C) A dual-task CNN optimized on both tasks performed and the separate networks (% top 1 accuracy on the test set). Error bars denote 95% confidence interval (CI) bootstrapped across classes and stimuli. Credit: <i>Science Advances</i> (2022). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abl8913 The spontaneous emergence of brain-like functional specialization in neural networks](https://scx1.b-cdn.net/csz/news/800a/2022/the-spontaneous-emerge.jpg)
The human brain has distinct and highly specialized functional regions to understand languages, recognize faces and plan ahead. However, neuroscientists must still decipher the high degree of functional specialization observed in the cortex. In a new study now published in Science Advances, Katharina Dobs and a team of scientists at the department of brain and cognitive sciences, MIT and the Zuckerman Mind Brain and Behavior Institute, Columbia University, New York, U.S., investigated face perception with artificial neural networks to test the hypothesis that functional segregation of facial recognition in the brain reflected computational optimization for broader applications of visual facial recognition. The team showed how functional visual segregation revealed a widespread tendency for optimization to create functional specialization in machines, and also further investigate the complexity of the phenomenon relative to brains.
Functional specialization
While the idea of functional localization in the brain was met with controversy for centuries, it is now supported with overwhelming evidence. Regions of the cortex can be selectively activated for a specific perceptual or cognitive task, which when disrupted can produce selective impairment. Neuroscientists increasingly aim to understand why the brain exhibits this level of functional specialization. Possibilities include an accident of evolution to easily add modules and solve new problems. Researchers have also highlighted selective modulation of mental processes via functional specialization. And a third possibility is the computational reasons to complete tasks that cannot be solved with comparatively generic machinery. In this work, Dobs et al. tested the third hypothesis to understand one of the best-established cases of functional specialization in the brain relative to visual recognition of faces. The team employed advanced deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to achieve human-level performance on some visual recognition tasks. Based on extensive studies with object-trained and face-trained networks on face and object recognition, Dobs et al. revealed a general tendency for task segregation in networks, opening the door to investigate specific architectures, and training diets to detect the tasks that will be segregated in networks, and hypothetically also in brains.
Networks trained only on objects do not perform well on face recognition
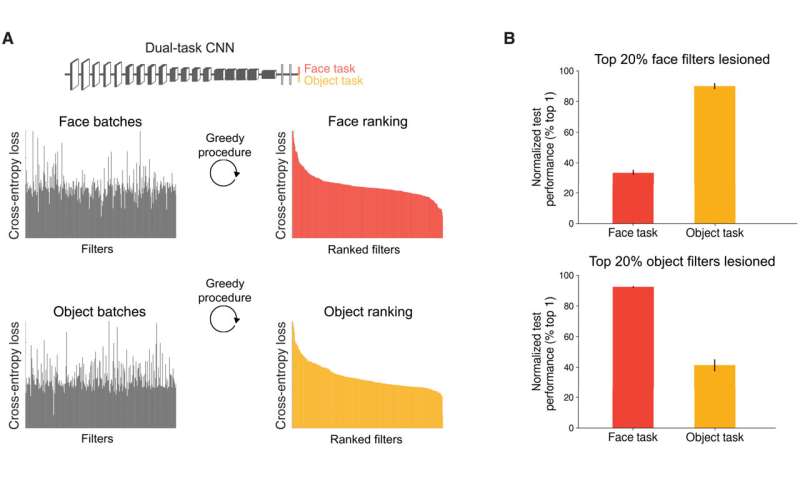
To test if the object-trained CNNs serve face recognition and vice-versa, Dobs et al. trained two randomly initialized VGG16 networks, as proposed initially by A. Zisserman and K. Simoyan from the University of Oxford, for face identification and object categorization. The team decoded unfamiliar face identities from face-trained networks and unfamiliar objects from the object-trained network, as expected. They noted significantly worse performance at face-recognition with the object-trained network than the face-trained network, and vice-versa for object recognition, indicating how representations learned for a specific-task did not readily translate to another task. Much like the brain, each task appeared to benefit from specialized task-specific representations.
Forming a dual-trained network
To circumvent limitations, Dobs et al. questioned if training a single network to perform both tasks would lead to discovering a common high-performing feature space for faces and objects. To address this, they trained a new network on both face identity and object categorization. The dual-task network unexpectedly performed nearly as well on each task, indicating a common feature space for the networks to solve both tasks, arguing against the hypothesis of functional specialization for high task performance. Another possibility was that the network learned to segregate itself into face and object recognition, although the team did not build anything into the network architecture to facilitate this. To test this possibility, they performed a series of experiments, and the results indicated spontaneous segregation of the network into distinct subsystems for face and object recognition, despite the lack of a task-specific, inductive bias to encourage the outcome.
Increased task segregation across layers like the brain
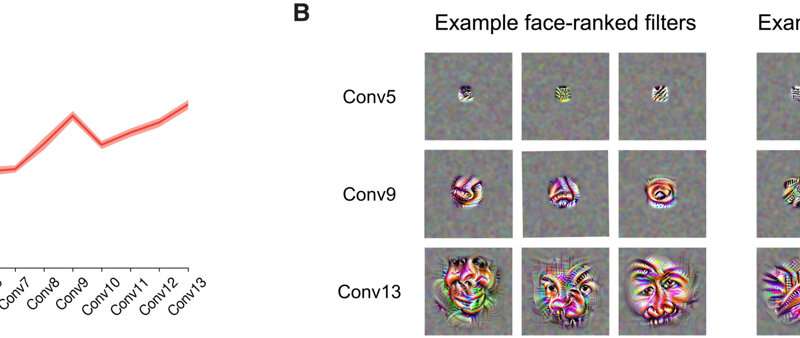
Dobs et al. next determined if task segregation built up on layers of the network. In primate brains, the usual categories are processed to share an initial set of common features, during early stages of processing (retina etc.), followed by branching into category-specific pathways (face, body, etc.). The team sought to understand such similarities with the dual-trained CNNs (convolutional neural networks) and found task segregation to be small in early layers, while increasing with later layers. According to the outcomes, processing of faces and objects gradually diverged at middle stages of processing within the network to become highly segregated in latter stages, much like those features observed in the primate brain. Further studies of the features highlighted the processing hierarchy. The outcomes showed that the observed high degree of functional segregation did not arise from dataset biases but were driven by distinct mid-to-high level visual features per task.
Functionally segregated networks and varying functional segregation
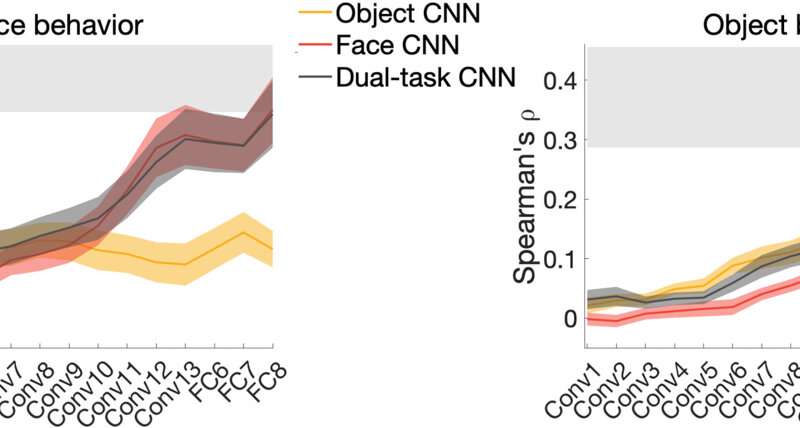
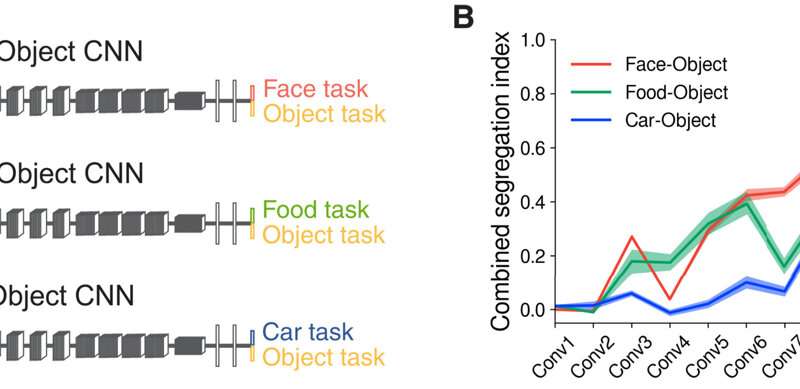
The work mirrored functional specialization in the human visual system, although it was unclear if the learned feature species could perform as similarly to the human visual system. To examine this, Dobs et al. ran two behavioral experiments to measure the perceived similarity of face and object stimuli. For each task, the team correlated the behavioral representation dissimilarity matrices of each participant for each layer of face-trained, object-trained and dual-task trained convoluted neural networks. The dual-task network captured human behavior in both face and tasks to show how learned solutions performed tasks similar to the human visual system and explored this setup for other visual categories. The outcome indicated that while functional segregation found in the brain could also be found in convoluted neural networks, brains did not entirely resemble the nuances of neural networks.
Outlook
Source: Read Full Article
