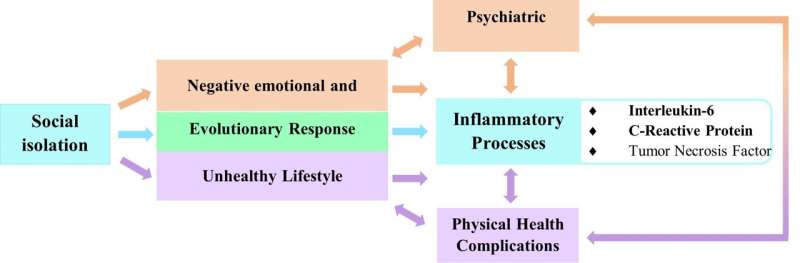
In a study published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, older US adults who experienced social isolation had higher blood levels of interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein, two markers of inflammation that can have long-term negative consequences for the health of individuals as they age.
The study included a nationally representative sample of 4,648 Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years and older.
The authors noted that clinical and social interventions that address social isolation among older adults may influence biological processes such as inflammation, as well as their potentially negative effects.
Source: Read Full Article
