Fat cells, or adipocytes, that grow in close proximity to breast cancers can shift into other cell types that promote tumor growth, a new study by UT Southwestern researchers suggests. The findings, published in Cell Reports, could lead to new ways to fight breast cancer, a disease that is diagnosed in more than 300,000 U.S. women each year and kills nearly 45,000 annually.
“We identified novel adipocyte-derived cell types in the mammary gland that offer a fertile soil for breast cancer tumor invasion and growth,” said study leader Philipp Scherer, Ph.D., Professor of Internal Medicine and Cell Biology and a member of the Harold C. Simmons Comprehensive Cancer Center at UTSW.
Obesity has long been considered a risk factor for breast cancer occurrence and worse prognosis. Studies have shown that fat cells in close contact with breast tumor cells have an enhanced ability to break down their lipids to provide fuel for invading tumor cells. However, Dr. Scherer explained, it has been unclear what other roles these adipocytes play in breast cancer progression.
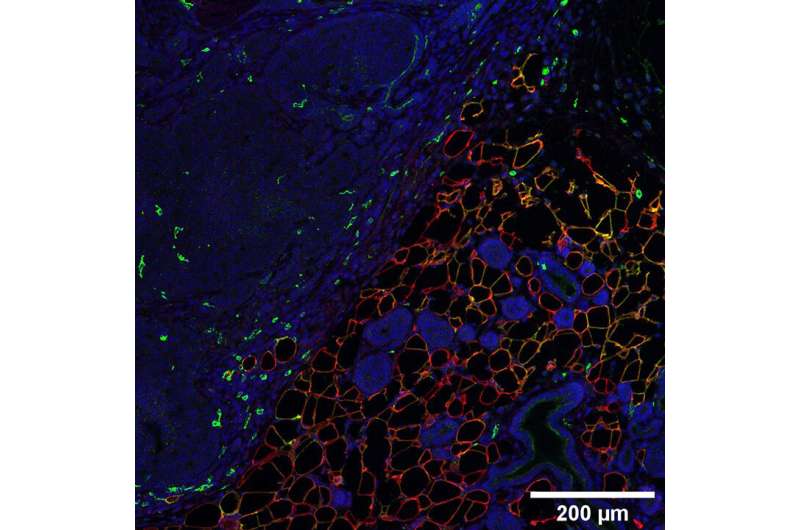
To answer this question, Qingzhang Zhu, Ph.D., an Instructor of Internal Medicine and member of the Scherer laboratory, and his colleagues used a genetic technique that “painted” adipocytes in lab mice so they glowed a fluorescent color, making it possible to follow these cells long term.
When the researchers implanted breast tumors in the mice or genetically manipulated the rodents’ own breast cells to turn them into tumor cells, they saw that nearby fat cells shrank and took on forms different from native adipocytes. Genetic testing to identify which genes were active in these fat cells showed these cells first regressed to an earlier stage in development, then gradually developed genetic markers of other cell types, including connective tissue cells, muscle cells, and immune cells.
Further investigation showed these changed fat cells encouraged breast cancer tumors to grow. However, this property also depended critically on their ability to supply energy to neighboring tumor cells. In addition, the properties of the cell types that fat cells morph into after they lose their lipids and their fat cell identity are important, since they add significantly to the local fibrosis, which contributes to the stiffness of breast tissue. When the researchers enhanced the lipid-storing capacity of mature fat cells, they ceased to morph into other cell types and no longer promoted tumor growth.
Source: Read Full Article
